- 반복자를 사용하여 집합 객체 내부 구조를 노출시키지 않고 순회하는 방법을 제공하는 행동 패턴(Behavioral Pattern)
- 집합체가 단일 책임 원칙을 최대한 지킬 수 있게 함
- 장점
- 집합체 클래스의 응집도를 높여줌
- 응집도 : 한 요소가 특정 목적을 위해 밀접하게 연관된 기능들이 모여서 구현되어 있을수록 높음
- 집합체에서는 항목에 접근하는 반복 작업에서 손을 떼고 이터레이터 객체에서 맡기 때문에 집합체의 인터페이스나 구현이 조금 더 간단해지고 원래의 목적에 맞게 클래스를 설계할 수 있음
- 집합체 클래스의 응집도를 높여줌
- 단점
- 단순히 순회작업을 위해 구현할 경우(뚜렷한 목적 없이) 클래스만 많아져 복잡도가 증가할 수 있음
Notice
Recent Posts
Recent Comments
Link
| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | ||||
| 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
| 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 |
| 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 |
| 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 | 29 | 30 | 31 |
Tags
- WKWebView
- 옵저버패턴
- 컴파운드패턴
- Scenedelegate
- 파사드패턴
- 추상팩토리패턴
- 데코레이터패턴
- 템플릿메서드
- Mobile
- 팩토리메서드패턴
- 컴포지트패턴
- ViewController
- 어댑터패턴
- 디자인패턴
- 이터레이터패턴
- RxSwift
- 커맨드패턴
- 스트래터지패턴
- 상태패턴
- 스테이트패턴
- DispatchQueue
- 싱글턴패턴
- 전략패턴
- ios
- 프록시패턴
- cocoapods
- Xcode
- SWIFT
- unowned
- Lifecycle
Archives
- Today
- Total
ios dev kangwook.
11. Iterator Pattern 본문
Iterator Pattern은 집합체의 구현 방법을 노출시키지 않고 그 안에 존재하는 모든 항목에 접근할 수 있도록 하는 패턴
Iterator Pattern
Iterator Pattern은 캡슐화를 통해 집합 객체의 요소에 순차적으로 접근할 수 있는 방법을 제공한다.
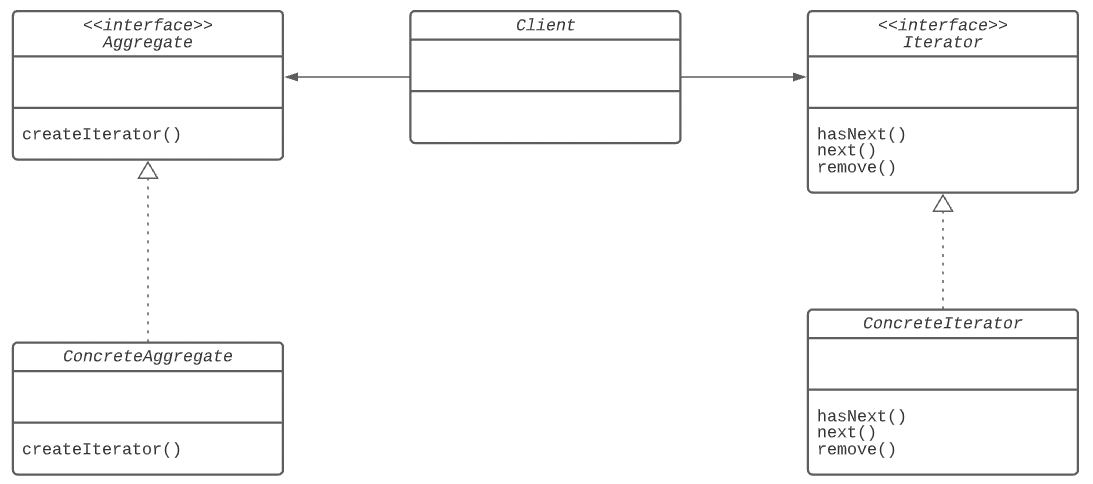
- Aggregate : 여러 요소들로 구성된 컬레션 인터페이스(데이터가 저장되어 있는 자료구조 → 집합체)
- ConcreteAggregate : Aggregate 인터페이스 구현체
- Iterator : 컬렉션의 요소들을 순서대로 검색하기 위한 인터페이스
- ConcreteIterator : Iterator 인터페이스 구현체
Iterator Pattern 예제
- 두 개의 서로 다른 식당이 있고 각각의 식당에서 메뉴를 조건에 따라 출력하는 예제
- 메뉴 아이템에 대한 정보를 담고 있는
public class MenuItem {
String name;
String description;
boolean vegetarian;
double price;
public MenuItem(String name, String description,
boolean vegetarian, double price) {
this.name = name;
this.description = description;
this.vegetarian = vegetarian
this.price = price;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public String getDescription() {
return description;
}
public double getPrice() {
return price;
}
public boolean isVegetarian() {
return vegetarian;
}
}- PancakeHouseMenu는 ArrayList를 통해서 메뉴를 구성하고 DinerMenu는 배열을 이용해서 메뉴를 구성
public class PancakeHouseMenu {
ArrayList<MenuItem> menuItems;
public PancakeHouseMenu() {
menuItems = new ArrayList<MenuItem>();
addItem("K&B's Pancake Breakfast",
"Pancakes with scrambled eggs, and toast",
true, 2.99);
addItem("Regular Pancake Breakfast",
"Pancakes with fried eggs, sausage",
false, 2.99);
addItem("Blueberry Pancakes",
"Pancakes made with fresh blueberries",
true, 3.49);
addItem("Waffles",
"Waffles, with your choice of blueberries or strawberries",
turne, 3.59);
}
public void addItem(String name, String description,
boolean vegetarian, double price) {
MenuItem menuItem = new MenuItem(name, description, vegetarian, price);
menuItems.add(menuItem);
}
public ArrayList<MenuItem> getMenuItems() {
return menuItems;
}
}
public class DinerMenu {
static final int MAX_ITEMS = 6;
int numberOfItems = 0;
MenuItem[] menuItems;
public DinerMenu() {
this.menuItems = new MenuItem[MAX_ITEMS];
addItem("Vegetarian BLT",
"(Fakin') Bacon with lettuce & tomato on whole wheat",
true, 2.99);
addItem("BLT",
"Bacon with lettuce & tomato on whole wheat",
false, 2.99);
addItem("Soup of the day",
"Soup of the day, with a side of potato salad",
false, 3.29);
addItem("Hotdog",
"A hot dog, with saurkraut, relish, onions, topped with cheese",
false, 3.05);
}
public void addItem(String name, String description,
boolean vegetarian, double price) {
MenuItem menuItem = new MenuItem(name, description, vegetarian, price);
if (numberOfItems >= MAX_ITEMS) {
System.err.prinln(
"Sorry menu is full Can't add item to menu");
} else {
menuItems[numberOfItems] = menuItem;
numberOfItems = numberOfItems + 1;
}
}
public MenuItem[] getMenuItems() {
return menuItems;
}
}- 두 메뉴를 사용하는 클라이언트(Waitress)를 작성
- 기능은 다음과 같이 정의
- printMenu() - 메뉴에 있는 모든 항목 출력
- printBreakfastMenu() - 아침 식사 항목만 출력
- printLunchMenu() - 점심 식사 항목만 출력
- printVegetarianMenu() - 채식주의자용 메뉴 항목만 출력
- isItemVegetarian(name) - name 항목이 채식주의자용이면 true 그렇지 않으면 false를 반환
- 기능은 다음과 같이 정의
- 각 메뉴에 있는 모든 음식을 출력하려면?
- 아이템에 대해서 반복적인 작업을 수행하기 위해 두 개의 반복문을 써야함
- 이후 식당이 더 추가된다면 이런 상황은 반복됨
PancakeHouseMenu pancakeHouseMenu = new PancakeHouseMenu();
ArrayList<MenuItem> breakfastItems = pancakeHouseMenu.getMenuItems();
DinerMenu dinerMenu = new DinerMenu();
MenuItem[] lunchItems = dinerMenu.getMenuItems();
for (int i = 0; i < breakfastItems.size(); i++) {
MenuItem menuItem = breakfastItems.get(i);
System.out.println(menuItem.getName());
SYstem.out.println(menuItem.getPrice());
System.out.println(menuItem.getDescription());
}
for (int i = 0; i < lunchItems.length; i++) {
MenuItem menuItem = lunchItems[i];
System.out.println(menuItem.getName());
System.out.println(menuItem.getPrice());
System.out.println(menuItem.getDescription));
}- 그래서 반복작업을 캡슐화하기 위해 Iterator 라는 객체를 만듦
- Java의 경우 Iterator라는 컬렉션을 제공
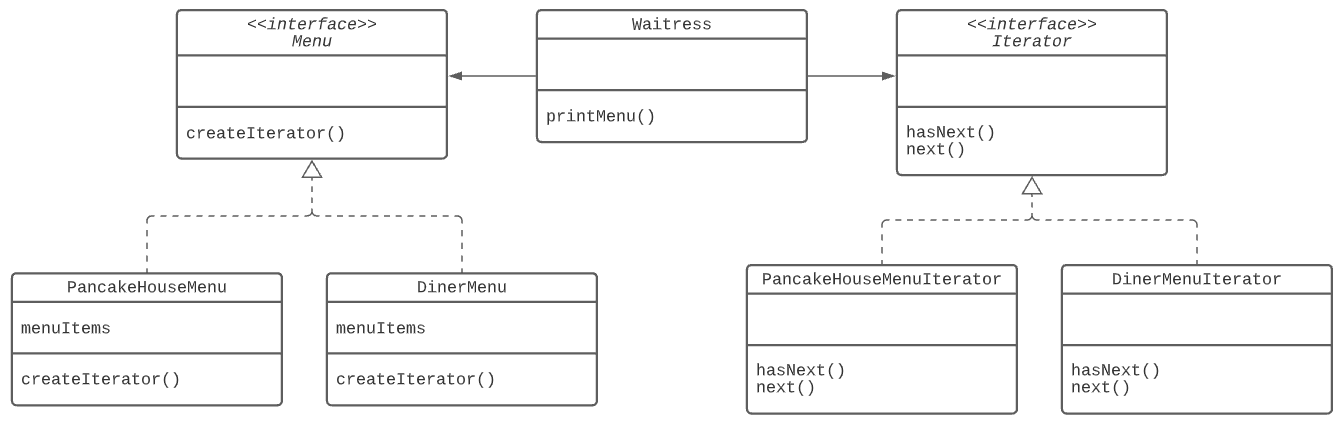
public interface Menu {
public Iterator<MenuItem> createIterator();
}
public class PankaceHouseMenu implements Menu {
ArrayList<MenuItem> menuItems;
public PancakeHouseMenu() {
this.menuItems = new ArrayList();
this.addItem("K&B's Pancake Breakfast",
"Pancakes with scrambled eggs, and toast",
true, 2.99);
this.addItem("Regular Pancake Breakfast",
"Pancakes with fried eggs, sausage",
false, 2.99);
this.addItem("Blueberry Pancakes",
"Pancakes made with fresh blueberries",
true, 3.49);
this.addItem("Waffles",
"Waffles, with your choice of blueberries or strawberries",
true, 3.59);
}
public void addItem(String name, String description,
boolean vegetarian, double price) {
MenuItem menuItem = new MenuItem(name, description, vegetarian, price);
menuItems.add(menuItem);
}
public ArrayList<MenuItem> getMenuItems() {
return menuItems;
}
@Override
public Iterator<MenuItem> createIterator() {
return menuItems.iterator();
// ArrayList 컬렉션은 반복자를 리턴하는 iterator()라는 메소드가 있음
}
}
public class DinerMenu implements Menu {
static final int MAX_ITEMS = 6;
int numberOfItems = 0;
MenuItem[] menuItems;
public DinerMenu() {
this.menuItems = new MenuItem[MAX_ITEMS];
addItem("Vegetarian BLT",
"(Fakin') Bacon with lettuce & tomato on whole wheat",
true, 2.99);
addItem("BLT",
"Bacon with lettuce & tomato on whole wheat",
false, 2.99);
addItem("Soup of the day",
"Soup of the day, with a side of potato salad",
false, 3.29);
addItem("Hotdog",
"A hot dog, with saurkraut, relish, onions, topped with cheese",
false, 3.05);
}
public void addItem(String name, String description,
boolean vegetarian, double price) {
MenuItem menuItem = new MenuItem(name, description, vegetarian, price);
if(numberOfItems >= MAX_ITEMS) {
System.err.println("Sorry menu is full Can't add item to menu");
} else {
menuItems[numberOfItems] = menuItem;
numberOfItems = numberOfItems + 1;
}
}
public MenuItem[] getMenuItems() {
return menuItems;
}
@Override
public Iterator<MenuItem> createIterator() {
return new DinerMenuIterator(menuItems);
}
}- 추가적으로 DinerMenuIterator라는 배열 순회 Iterator를 구현
public class DinerMenuIterator implements Iterator<MenuItem> {
MenuItem[] list;
int position = 0;
public DinerMenuIterator(MenuItem[] list) {
this.list = list;
}
@Override
public MenuItem next() {
MenuItem menuItem = list[position];
position += 1;
return menuItem;
}
@Override
public boolean hasNext() {
if(position >= list.length || list[position] == null) return false;
else return true;
}
}- Client인 Waitress클래스를 구현 - 이 과정에서 iterator를 이용해 메뉴를 출력
public class Waitress {
ArrayList<Menu> menus;
public Waitress(ArrayList<Menu> menus) {
this.menus = menus;
}
public void printMenu() {
Iterator menuIterator = menus.iterator();
while(menuIterator.hasNext()) {
Menu menu = menuIterator.next();
printMenu(menu.createIterator());
}
}
// method overloading
private void printMenu(Iterator<MenuItem> iterator) {
while(iterator.hasNext()) {
MenuItem menuItem = iterator.next();
System.out.println(menuItem.getName());
System.out.println(menuItem.getPrice());
System.out.println(menuItem.getDescription());
}
}
}- 메인 함수에서 테스트
- 이제 집합체 내에서 떤 식으로 일이 처리되는 지에 대해서 전혀 모르는 상태에서도 안에 들어있는 모든 항목들에 대해 반복작업을 수행할 수 있게 됨
public class MenuTest {
public static void main(String [] args) {
ArrayList<Menu> menuList = new ArrayList();
menuList.add(new PancakeHouseMenu());
menuList.add(new DinnerMenu());
Waitress waitress = new Waitress(menuList);
waitress.printMenu();
}
}결론
본문은 Head First Design Pattern (2004) 를 참고하여 공부하고 작성하였음
'Design Pattern' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 13. State Pattern (0) | 2022.09.05 |
|---|---|
| 12. Composite Pattern (0) | 2022.09.04 |
| 10. Template Method Pattern (0) | 2022.08.29 |
| 09. Facade Pattern (0) | 2022.08.27 |
| 08. Adapter Pattern (0) | 2022.08.23 |
Comments




